Deformation and Plastic Rotation Demand
The strain and plastic rotation demands are determined using the total displaced axis rotation θk obtained at the element end . Structure performance is determined as a result of unit strain and plastic rotation demands calculated by linear performance analysis in existing structures.
ICONS
h = Section height
L p = Plastic hinge length
M y = Effective yield moment
ϕ y = Yield curvature
ϕ t = Total curvature
θ p = Plastic rotation demand
θ y = Yield rotation
θ k = Displaced axis rotation
15.5.4. Determination of Unit Shape Deformation and Plastic Rotation Demands
15.5.4.1 - The unit deformation and plastic rotation demands of the element sections shall be determined by using the total displaced axis rotation θ k obtained at any element end as a result of the calculation made according to 4.7 or 4.8.2 . The definition of displaced axis rotations at the element ends is given in ANNEX 15A .
15.5.4.2 - total demand curve end section of the element φ t , Eq. (15.2) wherein the bond will be calculated.
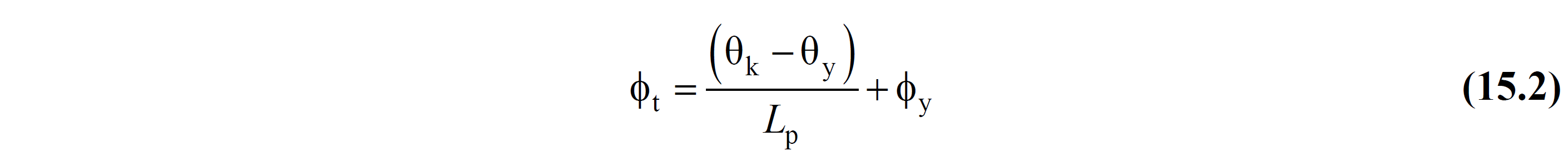
In Eq. (15.2) , θ y is the displaced axis yield rotation at the element end section , and ϕ y is the flow curvature at the element end section. The definition of displaced axis yield rotations at the element ends is given in ANNEX 15A . L p is the length of the plastic joint and shall be taken equal to half the cross-sectional dimension in the effective direction.
15.5.4.3 - Effective yield curvature ϕ y and effective yield moment M y in reinforced concrete systems will be calculated by moment curvature analysis.
15.5.4.4 - For confined or unconfined concrete and reinforcement steel models, if no other selection is made, ANNEX 5A can be used .
15.5.4.5 - plastic rotation lead section of element θ p , Eq. (15A.2) shall be obtained from.
Next Topic
