Commentary of Width-to-Thickness Limitations per AISC 341-16 with ideCAD
How does ideCAD control width-to-thickness Ratios according to AISC 341-16?
The width-to-thickness ratios of steel elements are automatically controlled and reported with steel elements reports according to Table D1.1.
Symbols
Fy = Specified minimum yield stress
Ry = Ratio of the expected yield stress to the specified minimum yield stress, Fy
Rt = Ratio of the expected tensile strength to the specified minimum tensile strength, Fu
Pa = Required axial strength using ASD load combinations, kips (N)
Pu = Required axial strength using LRFD load combinations, kips (N)
Py = Axial yield strength, kips (N)
Ca = Ratio of required strength to available axial yield strength
E= Modulus of elasticity of steel = 29,000 ksi (200 000 MPa)
Local buckling, when repeated like low-cycle fatigue caused by an earthquake, can cause very high localized stresses that can cause premature failure of an element intended to behave in a ductile manner. In order for horizontal structural system elements to achieve sufficient plastic deformation without local buckling under the effects of earthquakes, the width-thickness ratios of the compression elements must meet the conditions given in Table D1.1.
The width-to-thickness ratios of steel elements are automatically controlled and reported with steel elements reports according to Table D1.1.
Limiting Width-to-Thickness Ratios for Compression Elements for Moderately Ductile and Highly Ductile Members | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
Description of Element | Width-to- Thickness Ratio | Limiting Width-to-Thickness Ratio | Example | |
λhd | λmd | |||
Flanges of rolled or built-up I-shaped sections, channels and tees; legs of single angles or double-angle members with separators; outstanding legs of pairs of angles in continuous contact | b/t |
|
| 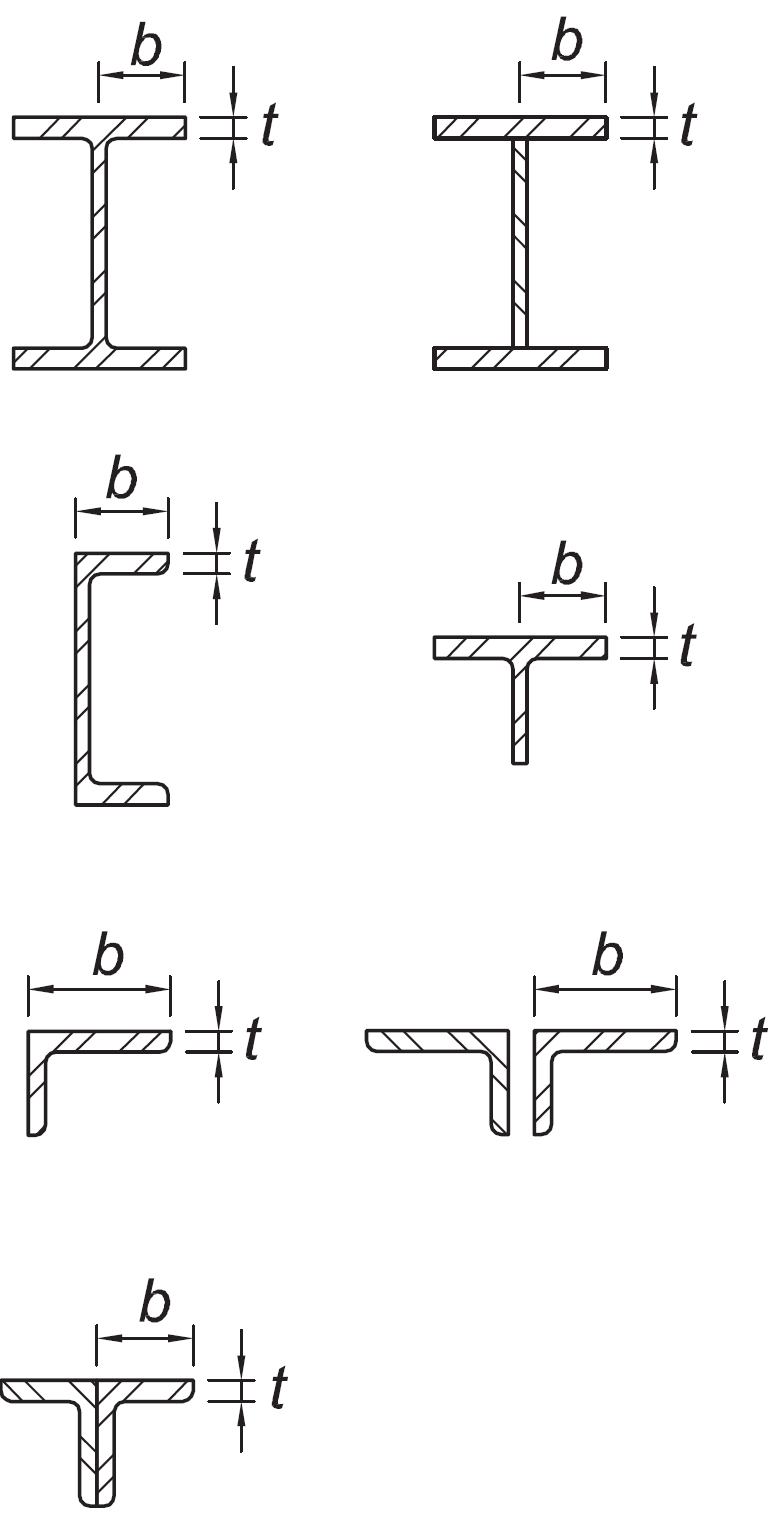 |
Flanges of H-pile sections per Section D4 | b/t | not applicable |
| 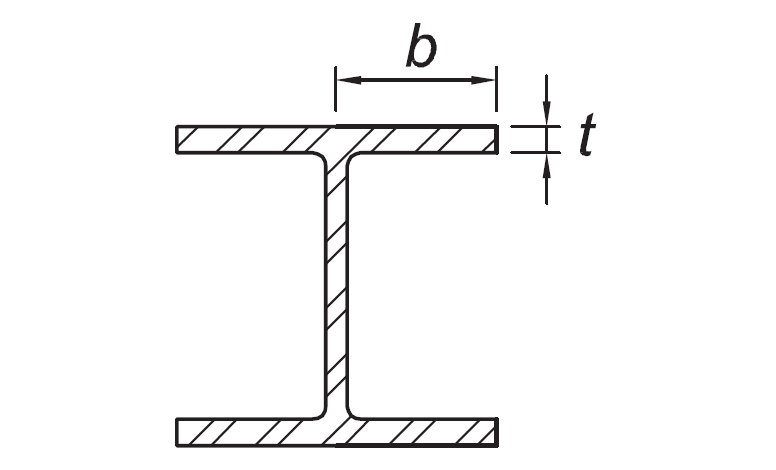 |
Stems of tees | d/t |
|
|  |
Walls of rectangular HSS used as diagonal braces | b/t |
|
| 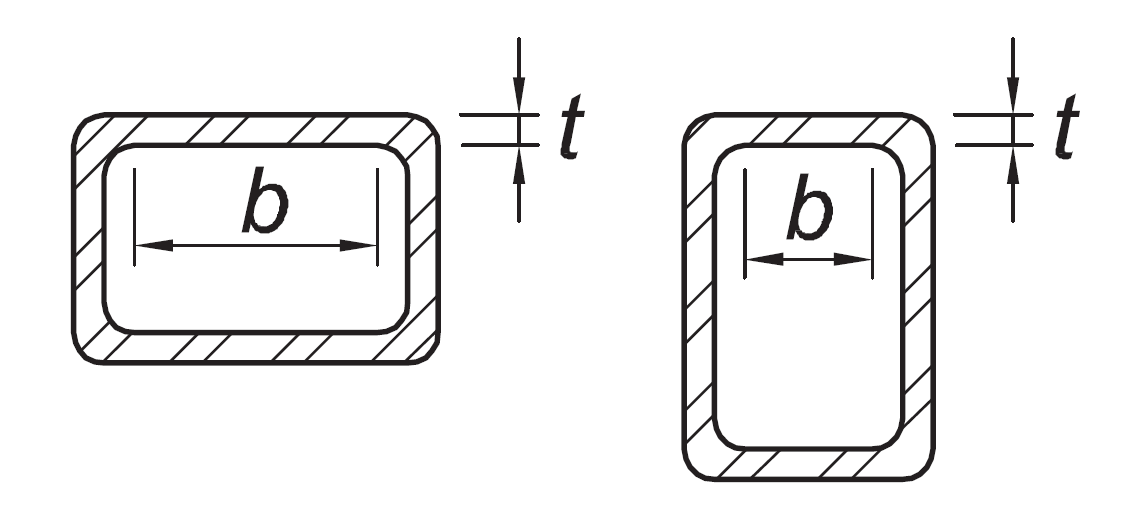 |
Flanges of boxed I-shaped sections | b/t |
|
| 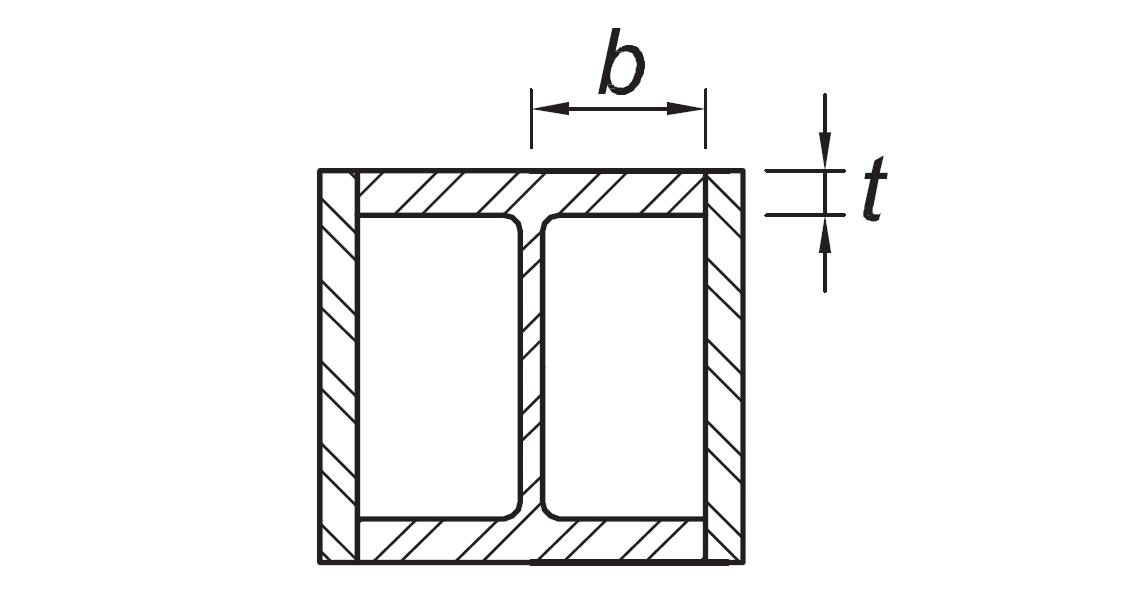 |
Side plates of boxed I-shaped sections and walls of built-up box shapes used as diagonal braces | h/t |
|
| 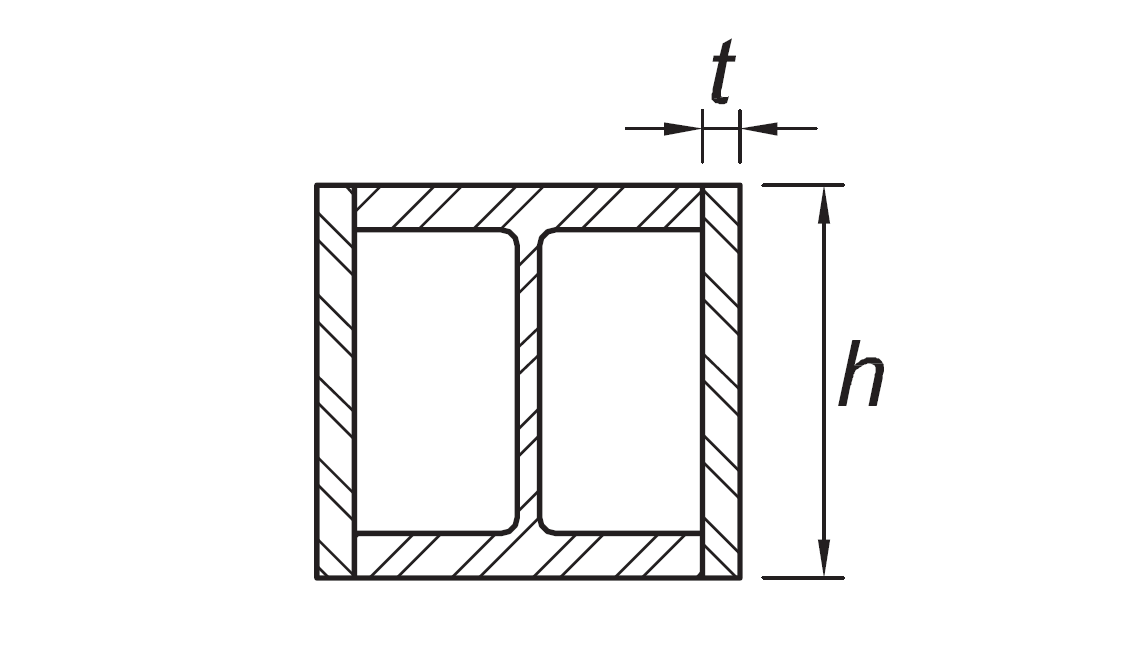 |
Flanges of built up box shapes used as link beams | b/t |
|
| 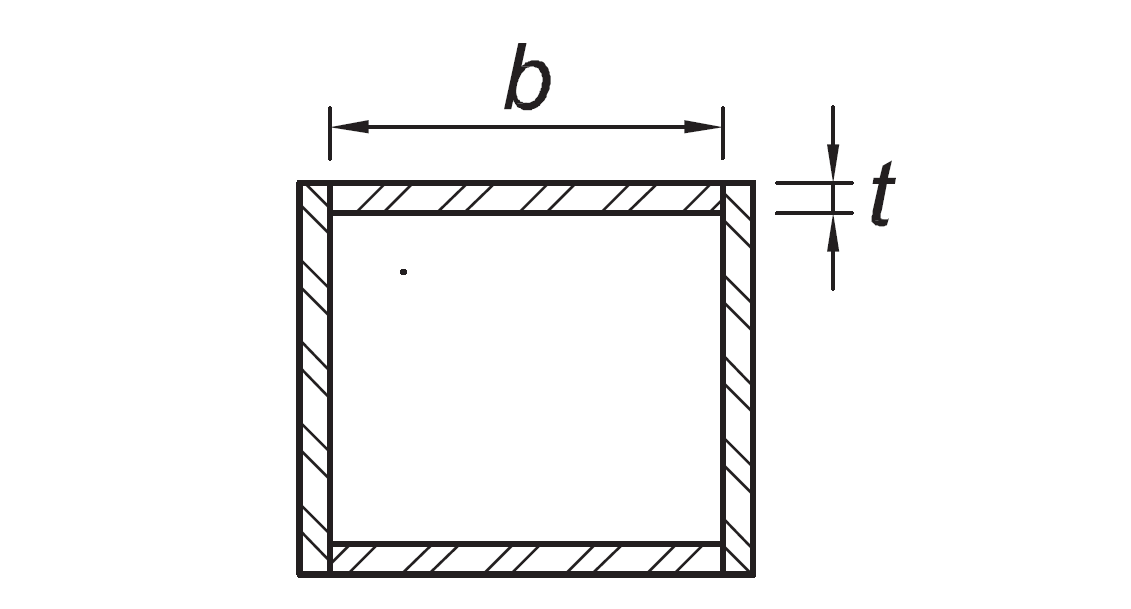 |
Webs of rolled or built-up I shaped sections and channels used as diagonal braces | hw/t |
|
| 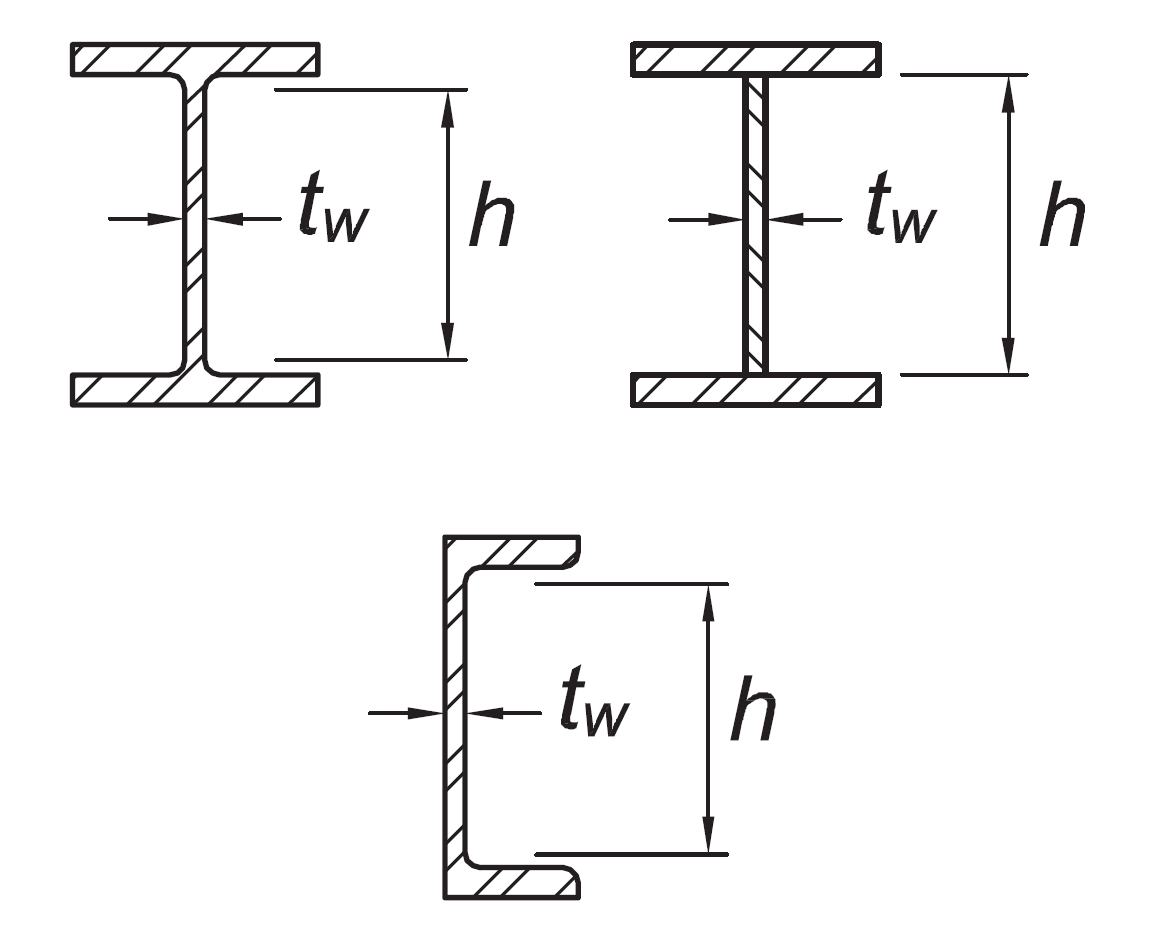 |
Where used in beams or columns as flanges in uniform compression due to axial, flexure, or combined axial and flexure:
| b/t h/t |
|
| 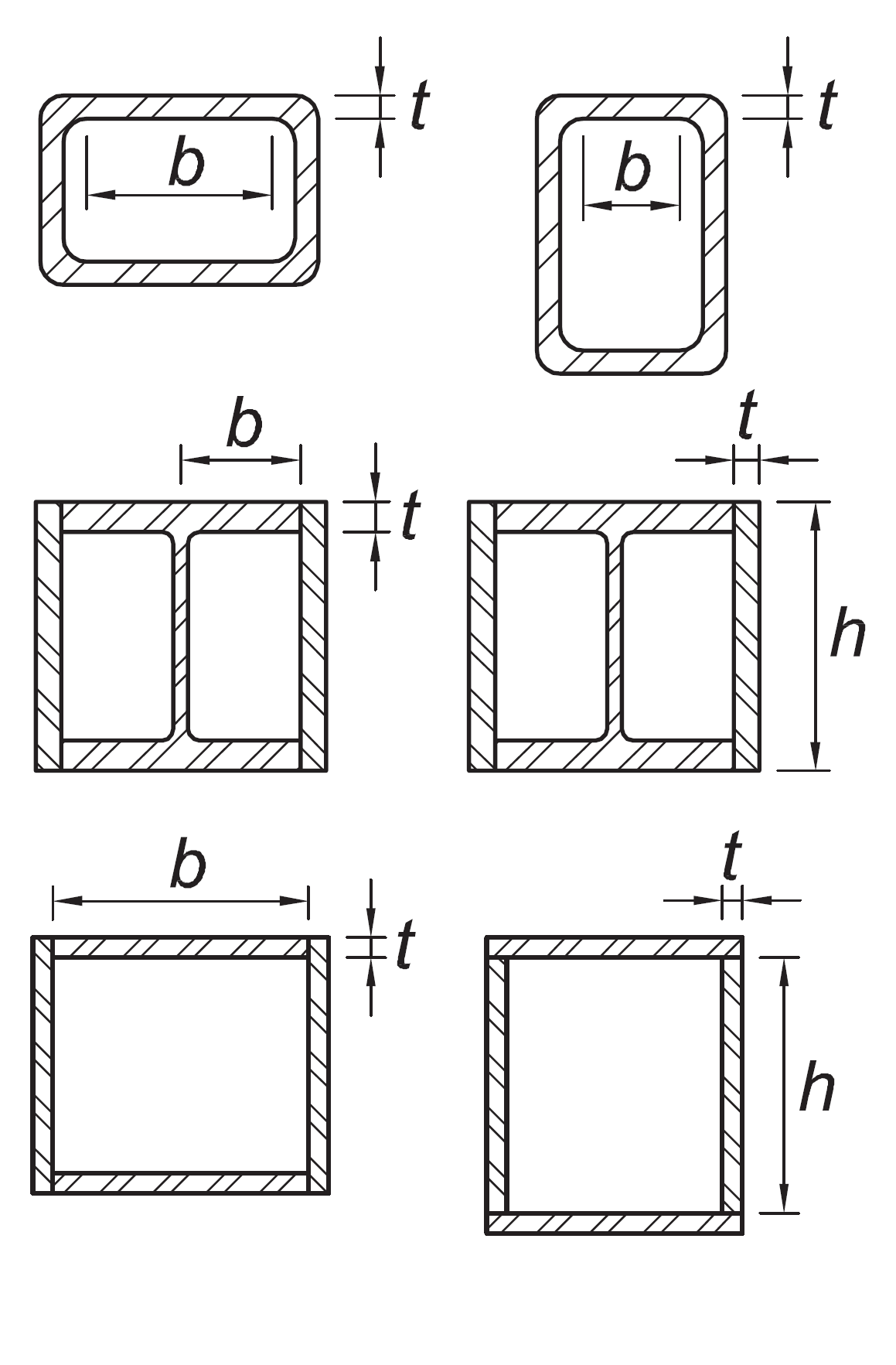 |
Where used in beams, columns, or links, as webs in flexure, or combined axial and flexure:
| h/tw h/t h/t | For Ca ≤ 0.114 For Ca > 0.114 where | For Ca ≤ 0.114 For Ca > 0.114 where | 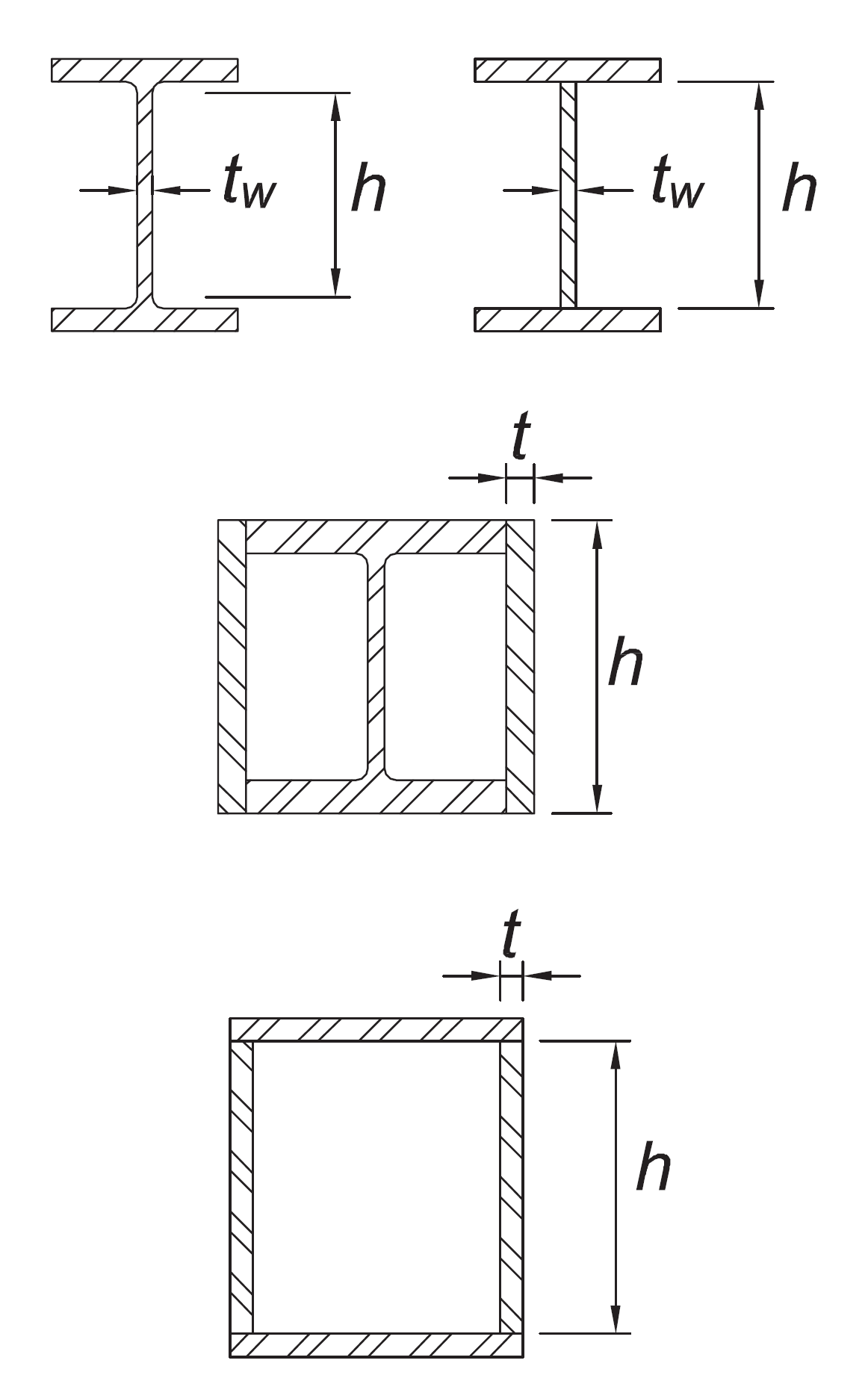 |
Webs of built-up box sections used as EBF links | h/t |
|
| 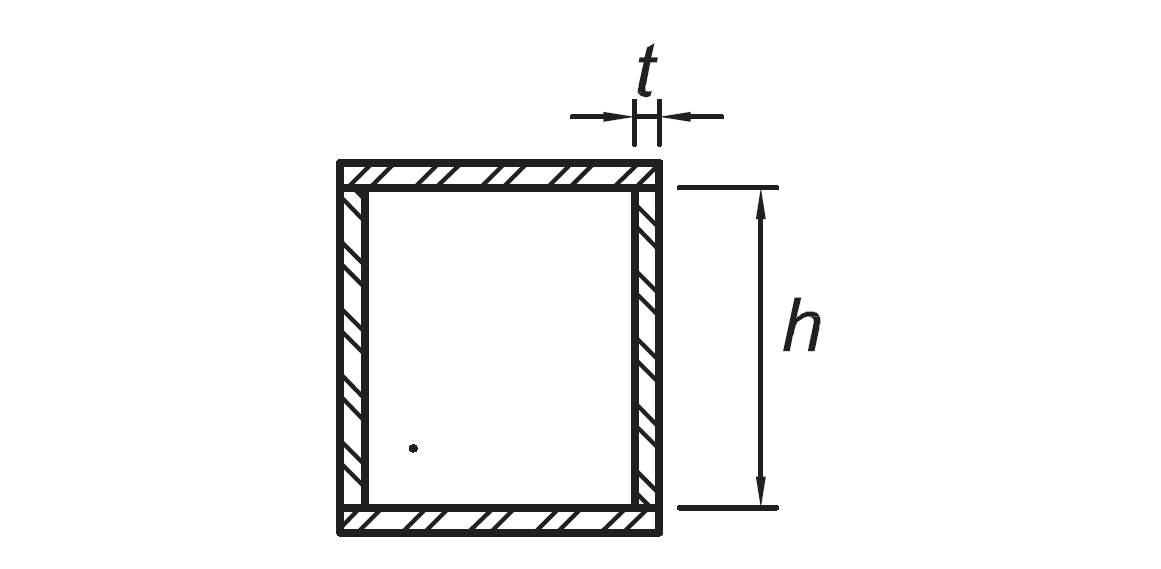 |
Webs of H-Pile sections | h/tw | not applicable |
| 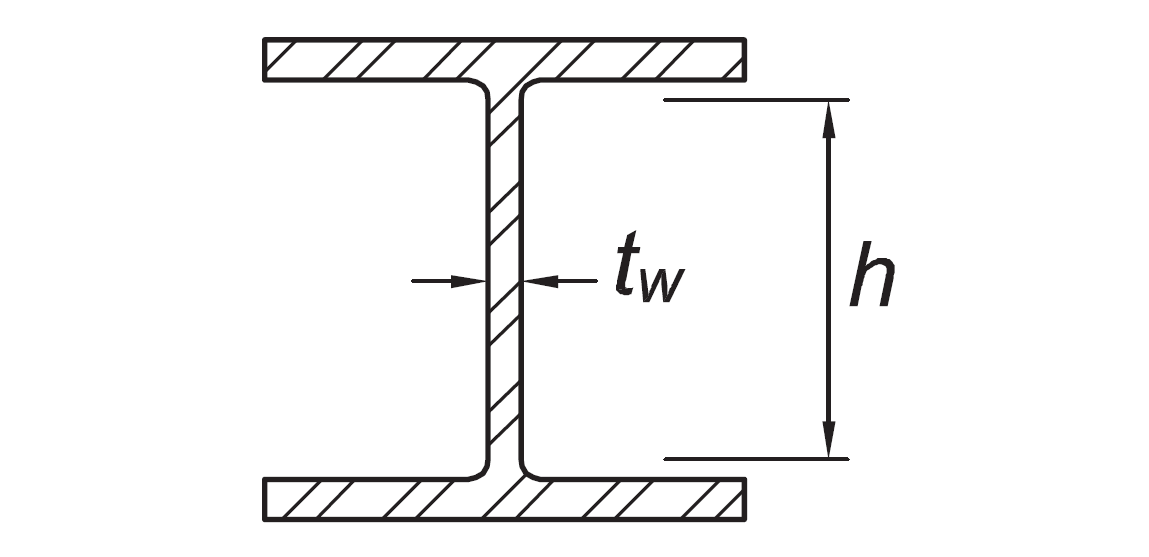 |
Walls of round HSS | D/t |
|
| 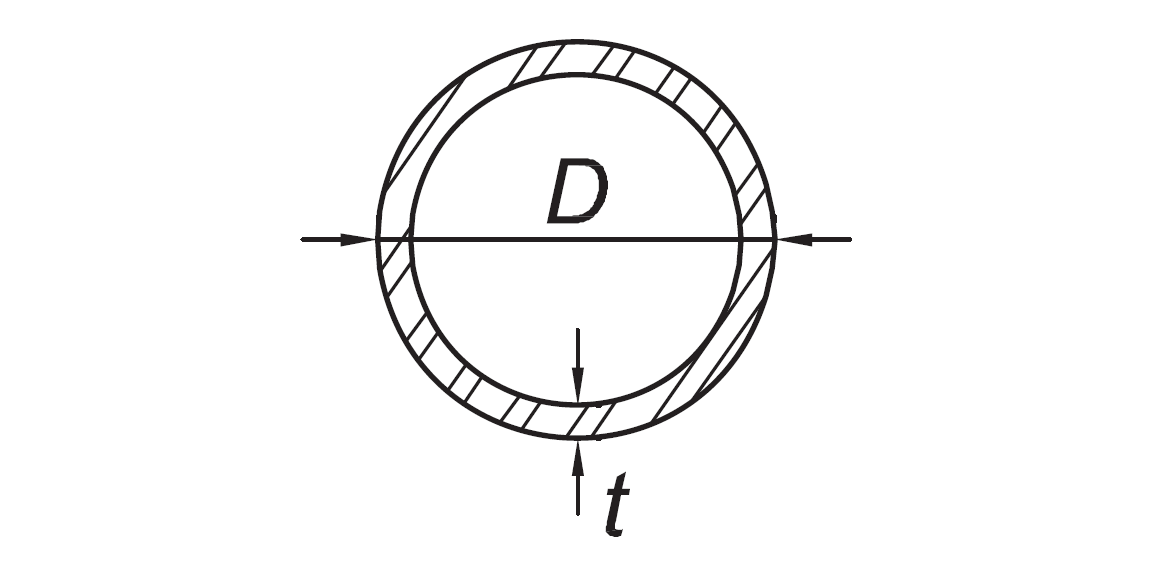 |
