Castellated Beam Design
Castellated Beam Sections
Hexagonal, circular, octagonal-shaped hollow, and Angelina sections can be defined. Hexagonal and circular hollow sections are designed.
Download ideCAD for AISC 360-16
Biaxial Bending and Axial Compression Control
Yielding Limit State
For the yielding limit state, the solid element's characteristic bending moment strength Mn is found in accordance with ÇYTHYEDY.

In case of Lb<Lp
The element is safe against the lateral-torsional buckling limit state and the bending moment strength can be calculated according to Equation 9.2.
In case of Lp<Lb<Lr
Considering the lateral-torsional buckling limit state, the bending moment strength Mn can be calculated as follow:
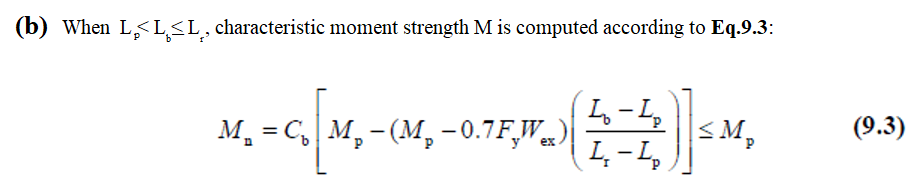
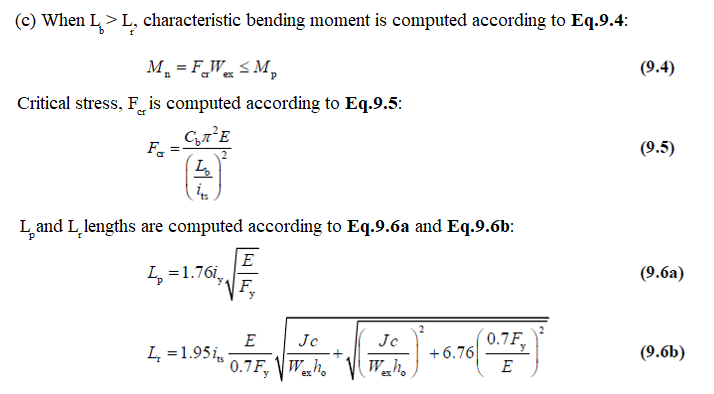
In case of Lb>Lr
Considering the elastic-buckling of the element, the bending moment strength Mn can be calculated as follow:
Axial Compression
The axial compression capacity for the solid element part of the castellated beam can be calculated as follow:

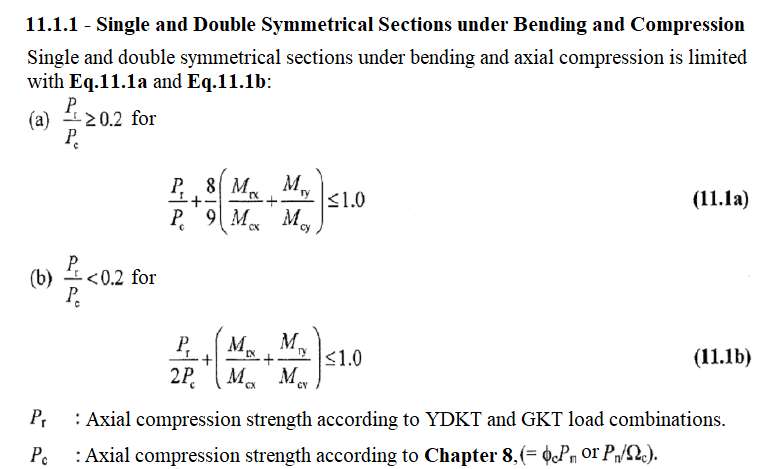
Combined Effects
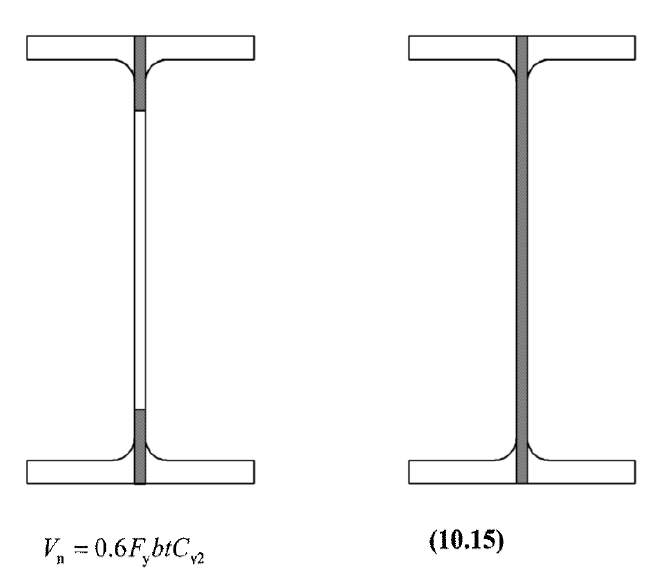
Shear Control
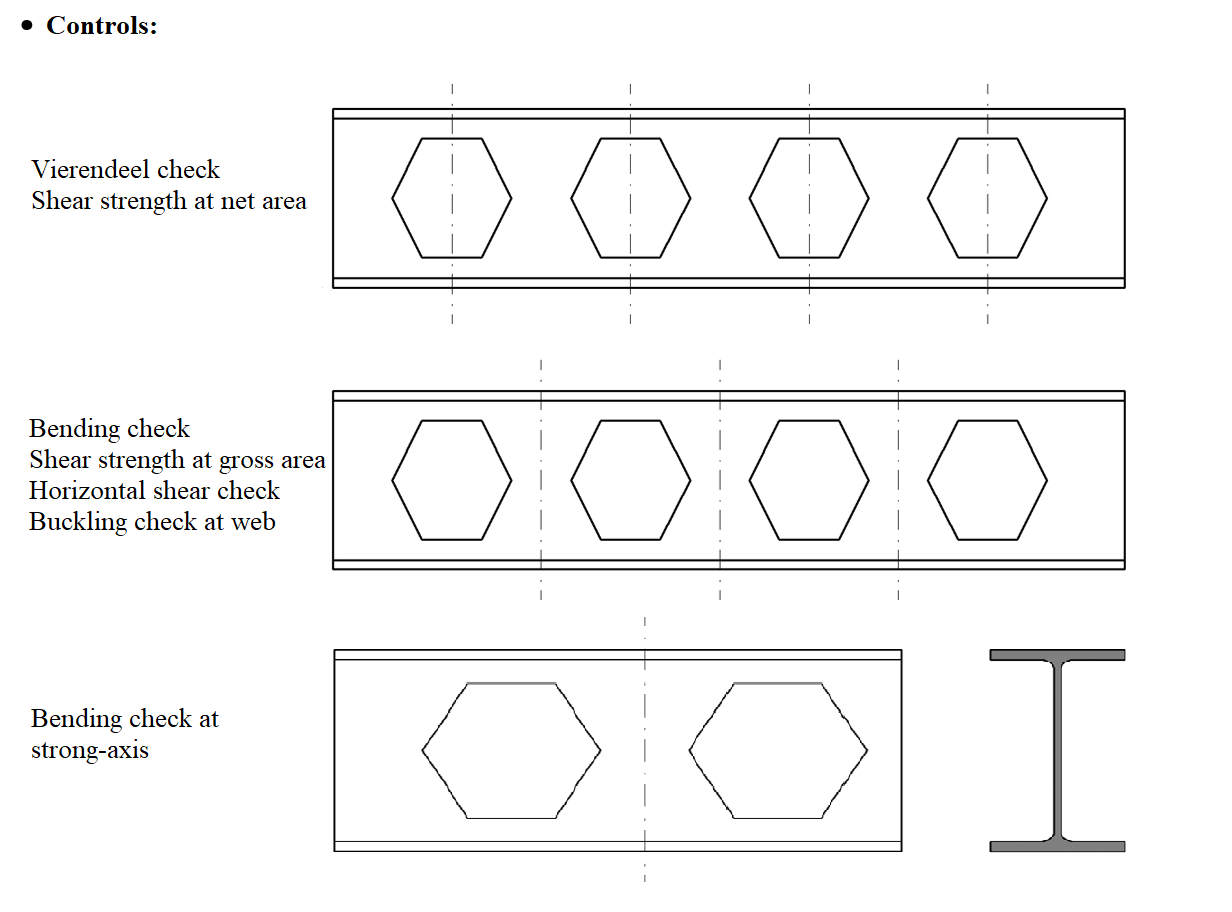
Gross and Net Area for Shear Control
The gross shear area is the full web part of the castellated beam and the net shear area is calculated by taking into account the hollow parts of the castellated beam as follow:
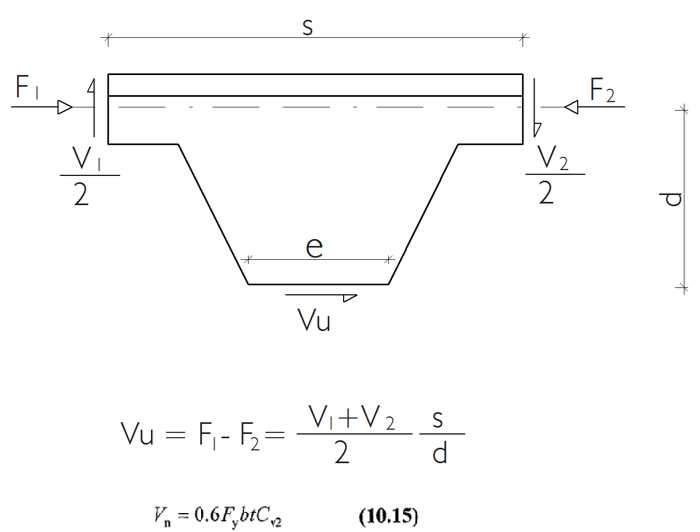
Horizontal Shear Control
The shear force on the castellated beam web is calculated using the equilibrium equation and compared with the shear strength.
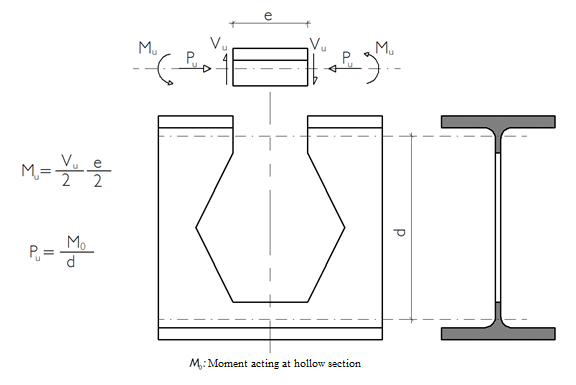
Vierendeel Control
Biaxial Bending and Axial Compression Effects
The loads on the T section that is above of the castellated beam hollow are found with the assistance of equilibrium equations. While calculating these forces, internal force diagrams in the static analysis are used. The bending moment and axial force on the T section are calculated by the equilibrium equations. Then the combined effects are considered by finding the bending and axial force strengths of the T-section.

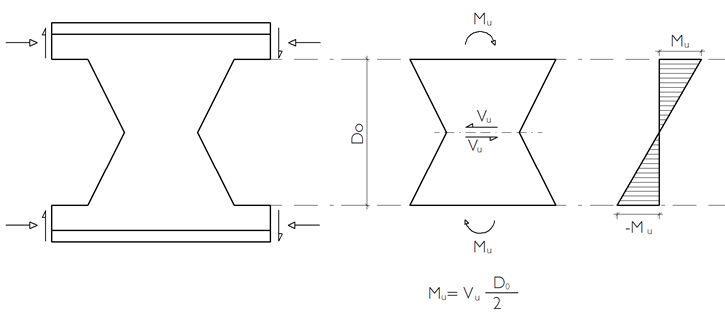
Web Buckling Control
Forces Acting on the Web
The bending moment values at the upper and lower boundaries of the solid web section between the castellated beam hollows are found and lateral-torsional buckling is controlled according to the rectangular section.
Web Buckling Strength
The solid web section between the castellated beam hollows is calculated according to ÇYTHYEDY 9.11.

