Example 1 for Lamda Coefficient used in Story Drift Determination
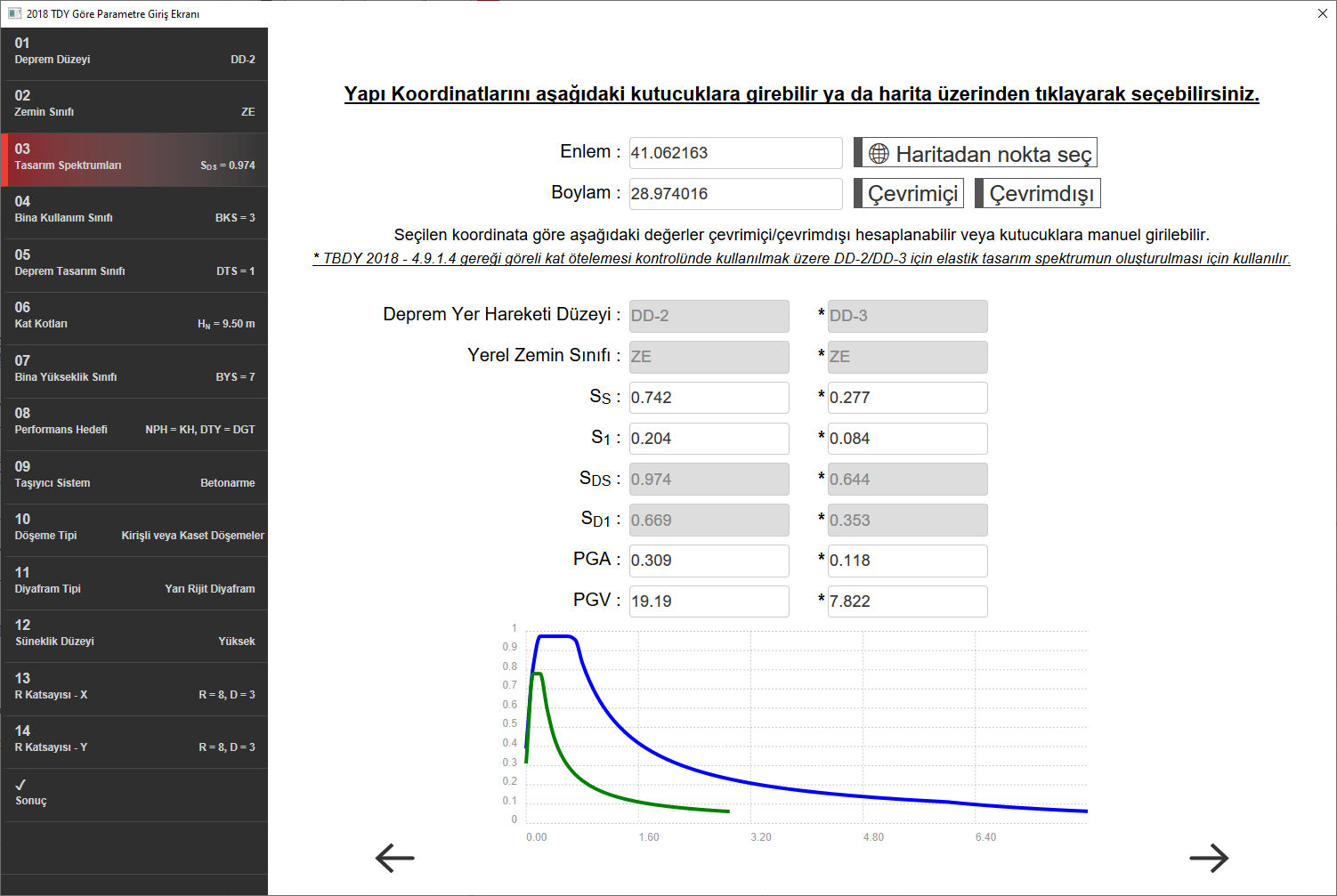
DD2 default values
SDS =0.974
SD1 = 0.669
Ta = 0.2 * SD1 / SDS = 0.2 * 0.669 / 0.974 = 0.137
Tb = SD1 / SDS =0.669 / 0.974 =0.686
DD3 default values
SDS=0.644
SD1=0.353
Ta = 0.2 * SD1 / SDS = 0.2 * 0.353 / 0.644 = 0.109
Tb = SD1 / SDS =0.353 / 0.644 =0.548
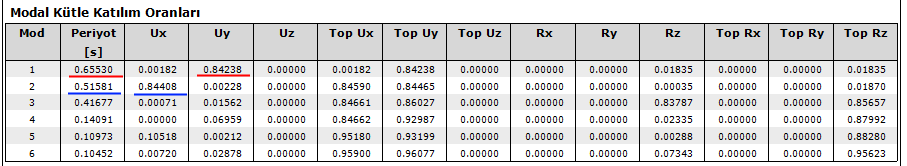
From the dynamic analysis, by reading the highest modal participation ratios in accordance with its direction in E1, E2, E3 and E4 loading, the dominant vibration periods for each x and y direction are determined. Among the 4 periods determined for the X direction, the one with the highest mass participation ratio is selected. The same is done in the Y direction.
Capital E1
Capital E2
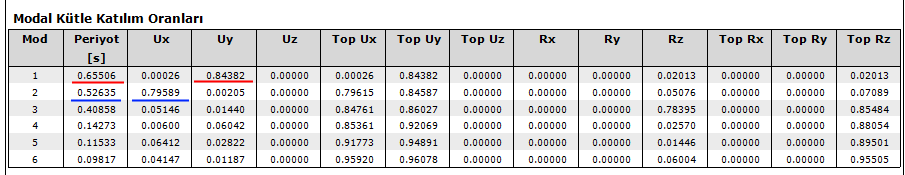
Modal E3
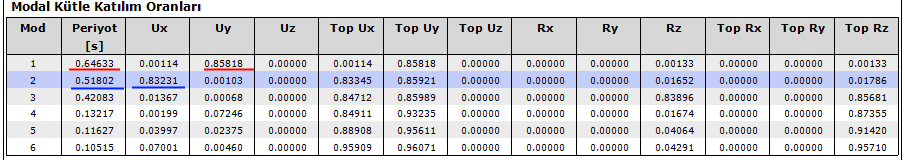
Modal E4
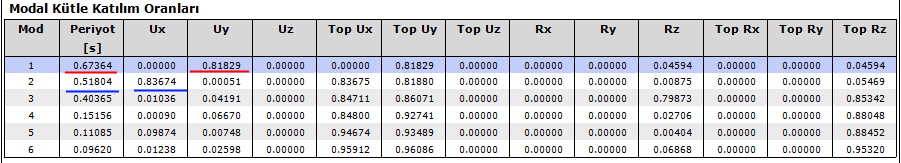
Modal E1 → T = 0.51581 sec for x direction
Modal E3 → T = 0.64633 sec for y direction
Finding Sae (T) values
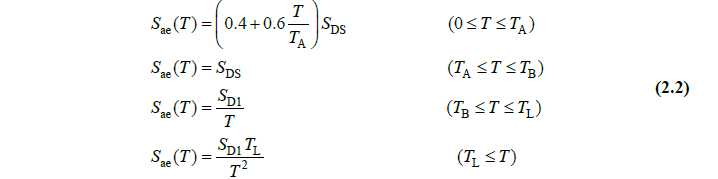
Calculation for X Direction
DD3
For T = 0.51581 sec
Ta= 0.106 < T=0.51581 < Tb=0.548 -> Sae(T)=SDS= 0.644
LO2
For T = 0.51581 sec
Ta= 0.137 < T= 0.51581 < Tb=0.686 -> Sae(T)=SDS = 0.974
Lamda = 0.644 / 0.974 =0.661
Calculation for Y Direction
DD3
For T = 0.64633 sec
T=0.64633 > Tb=0.548-> Sae(T)=SD1/T= 0.353/ 0.64633=0.546
LO2
For T = 0.64633 sec
Ta=0.137 < T =0.64633 < Tb=0.686 -> Sae(T)=SDS=0.974
Lamda = 0.546 / 0.974=0.5605
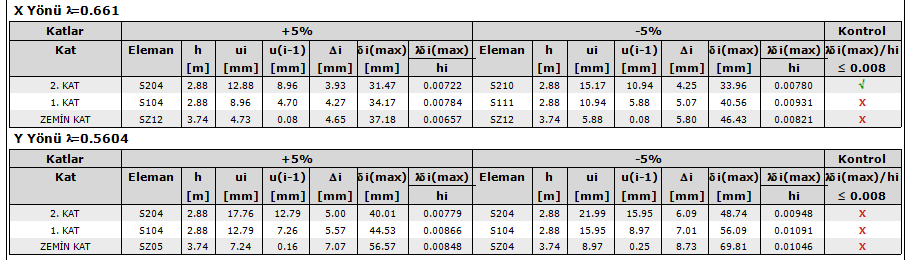
X direction 1st Floor - 5% -> 0.661 * 40.56 / 2880 = 0.00931> 0.008 not provided
Y direction 1st floor - 5% -> 0.5605 * 56.09 / 2880 = 0.01091> 0.008 not provided